Iran's Shia Majority: Culture, Policy, & Global Impact
Iran stands as a unique nation in the Middle East, primarily defined by its overwhelming adherence to Shia Islam. This profound religious identity is not merely a demographic statistic; it is the very bedrock upon which Iran's culture, domestic policies, and intricate foreign relations are built. Understanding the dynamics of the Shia population in Iran is crucial for anyone seeking to grasp the complexities of this influential country.
From its ancient Persian heritage to its modern revolutionary spirit, the predominantly Shia character of Iran has shaped its trajectory in ways few other nations experience. It distinguishes Iran from many of its Sunni-majority neighbors and forms the basis for both its alliances and its rivalries on the global stage. This article delves deep into the demographics, historical context, and far-reaching implications of Iran's significant Shia population.
Table of Contents
- The Heart of Shia Islam: Iran's Demographic Landscape
- Unpacking Iran's Shia Majority: Numbers and Estimates
- The Dominant Twelver Shia: Iran's Official State Religion
- Beyond the Majority: Sunni Minorities in Iran
- The Profound Impact of Shia Identity on Iran
- Iran's Foreign Policy: Shaped by Shia Solidarity
- Global Shia Distribution: Iran in a Wider Context
- Understanding Iran's Religious Fabric: A Holistic View
The Heart of Shia Islam: Iran's Demographic Landscape
Iran, a nation with an estimated population of 87.6 million as of mid-2023, stands as a pivotal center for Shia Islam globally. While Islam is the predominant religion, with Muslims constituting 99.4 percent of the population according to Iranian government estimates, it is the specific branch of Islam that truly defines Iran's unique character. The vast majority of Iranians identify as Shia Muslims, making the Shia population in Iran one of the largest and most concentrated in the world. This demographic reality is not a mere footnote; it is the fundamental lens through which Iran's societal norms, political structures, and international relations are viewed and understood. The nation's identity is inextricably linked to its Shia heritage, influencing everything from daily life to its strategic geopolitical maneuvers.Defining Shia and Sunni Islam: A Brief Overview
To fully appreciate the significance of the Shia population in Iran, it's essential to understand the fundamental distinction between Shia and Sunni Islam. These are the two main branches of Islam, emerging from a historical disagreement over the succession to Prophet Muhammad. Sunni Muslims, who constitute a commanding majority (85% to 90%) of the world's Muslim population, believe that the Prophet's successor should be chosen by consensus. Shia Muslims, on the other hand, believe that leadership should have remained within the Prophet's family, specifically through his son-in-law and cousin, Ali ibn Abi Talib, and his descendants. This theological divergence has led to distinct interpretations of Islamic law, religious practices, and political thought. While both branches share core Islamic beliefs, their historical trajectories and theological nuances have led to different cultural and political expressions across the Muslim world. Iran's embrace of Shia Islam, particularly the Twelver branch, sets it apart from many of its neighbors and the broader global Muslim community.Unpacking Iran's Shia Majority: Numbers and Estimates
The statistical data regarding the Shia population in Iran consistently highlights its overwhelming dominance. According to Iranian government estimates, between 90 to 95 percent of the country's Muslim population are Shia. This figure is significant, especially when considering the total Muslim population was estimated at 99.4% in 2011. The remaining 0.6% of the total population comprises other religious groups, including Zoroastrian, Jewish, and Christian communities, each making up a small fraction. This means that a substantial majority of the entire Iranian populace adheres to Shia Islam. While specific figures for 2025 regarding the exact percentage of Iran's population belonging to the Shia branch are anticipated, the consistent reporting indicates a deeply entrenched Shia identity that has remained stable over decades. The prevalence of Shia Islam is not just a statistical fact but a lived reality that permeates every aspect of Iranian society.Official Figures vs. Global Perspectives
While Iranian government estimates provide a clear picture of the Shia population in Iran, it's worth noting how these figures align with broader global statistics. International reports and analyses generally corroborate the notion of Iran as a predominantly Shia nation. For instance, the data indicates that Shia Muslims form a majority of the population in only three countries across the Muslim world, with Iran being the most prominent among them, alongside Iraq and Bahrain. This underscores Iran's unique demographic profile. Although earlier reports from certain sites did not always break down the Muslim population by Shia and Sunni percentages, more recent government estimates consistently affirm the 90-95% Shia majority. This consistent reporting across various sources solidifies the understanding that Iran is, by an overwhelming margin, a Shia-dominated country, a fact that profoundly influences its internal governance and external posture.The Dominant Twelver Shia: Iran's Official State Religion
Within the broader spectrum of Shia Islam, the vast majority of Iranians adhere to the Ithnā ʿAsharī, or Twelver, Shiʿi branch. This specific denomination is not merely the dominant religious affiliation; it is the official state religion of Iran. Twelver Shia Islam holds a unique position in Iran, deeply embedded in its constitutional framework and legal system since the 1979 Islamic Revolution. The Twelvers believe in twelve divinely ordained Imams, successors to Prophet Muhammad, the last of whom, Muhammad al-Mahdi, is believed to be in occultation and will return as the Mahdi. This belief system profoundly influences the political theology of the Islamic Republic, where the concept of the "Guardianship of the Islamic Jurist" (Velayat-e Faqih) serves as the guiding principle, representing the rule of the supreme religious leader in the absence of the hidden Imam. This institutionalization of Twelver Shia Islam ensures that the religious identity of the Shia population in Iran is not just a matter of personal faith but a foundational element of national governance and identity. Other main Shia branches, such as Isma'ilism and Zaydism, exist but are far less prevalent in Iran compared to Twelverism.Beyond the Majority: Sunni Minorities in Iran
While the Shia population in Iran constitutes the overwhelming majority, it is important to acknowledge the presence of a significant Sunni Muslim minority. According to Iranian government estimates, Sunnis make up between 5% and 10% of the Muslim population. This percentage, though small in comparison to the Shia majority, represents several million individuals within Iran's total population. Unlike the homogenous Shia majority, most Sunni Muslims in Iran belong to distinct ethnic minority groups. This intersection of religious and ethnic identity adds another layer of complexity to Iran's social fabric. Understanding the distribution and experiences of these Sunni communities is crucial for a complete picture of religious diversity within the country.Ethnic Diversity and Religious Affiliation
The distribution of Sunni Muslims in Iran is largely concentrated among specific ethnic groups. For instance, the Kurds, primarily residing in western Iran, are predominantly Sunni Muslims. Similarly, the Turkmen, found in the northeastern regions, also largely adhere to Sunni Islam. Iran's Arab population, situated mainly in the southwest, presents a more mixed picture, with communities that are both Sunni and Shiʿi. The province of Kermanshah, for example, is noted to have a population where thirty percent is composed of Sunnis, highlighting regional variations in religious demographics. This strong correlation between ethnic identity and religious affiliation means that discussions about religious minorities in Iran often intertwine with issues of ethnic identity and regional autonomy. While the state religion is Twelver Shia Islam, the presence of these Sunni ethnic groups contributes to the rich, albeit sometimes complex, tapestry of Iran's diverse population. Alongside these Muslim communities, small communities of Christians, Jews, and Zoroastrians are also found throughout the country, further adding to its religious pluralism.The Profound Impact of Shia Identity on Iran
The numerical dominance of the Shia population in Iran has a profound and pervasive impact on virtually every aspect of the nation's existence. This Shia majority profoundly impacts Iran’s culture, domestic policies, and its societal norms. Culturally, Shia rituals and holidays, such as Ashura and Arbaeen, are central to the national calendar and public life, often involving large-scale public mourning and processions that reinforce collective identity and historical narratives. Religious institutions, particularly seminaries in cities like Qom, hold immense influence, shaping educational curricula, legal interpretations, and moral guidelines. Domestically, the principles of Twelver Shia Islam are enshrined in the constitution, influencing laws related to family, crime, and public conduct. The legal system is based on Islamic jurisprudence, and the supreme leader, a Shia cleric, holds ultimate authority, ensuring that governance aligns with Shia Islamic tenets. This deep integration means that understanding the Shia population in Iran is not just about numbers; it's about comprehending the very soul of the nation and the guiding principles that govern its citizens' lives.Iran's Foreign Policy: Shaped by Shia Solidarity
The predominantly Shia character of Iran has historically created complexities in its relationships with neighboring countries and profoundly shaped its foreign policy strategies. In regions where Sunni Islam is prevalent, Iran has sometimes faced isolation, with its unique religious identity often perceived as a challenge to the regional status quo. This has defined the manner in which Iran forms its relations with adjacent countries, leading to a foreign policy that often prioritizes alliances based on shared religious or ideological grounds. The concept that "there is no difference between Islam in Iran and in any other Muslim country" is a myth, as Iran's distinct Shia identity inherently differentiates its approach to regional and global affairs. This religious distinction is a cornerstone of its strategic thinking, guiding its alliances and interventions across the Middle East.Strategic Alliances and Regional Complexities
Iran actively cultivates strong ties with nations possessing meaningful Shia communities, fostering collaborative relationships based on shared religious and strategic interests. Currently, Iran sponsors the Shia population and militias in different states in the Middle East, including Iraq, Lebanon, and Yemen. In Iraq, Iran's influence is significant, particularly among Shia political and paramilitary groups, reflecting a shared religious heritage and strategic alignment against perceived common adversaries. In Lebanon, Iran's long-standing support for Hezbollah, a powerful Shia political party and militant group, is a clear manifestation of this policy. Similarly, in Yemen, Iran has supported the Houthi movement, a Zaydi Shia group, in its conflict, further extending its regional influence through religious solidarity. These relationships are not merely acts of religious patronage; they are strategic alliances that allow Iran to project power, counter rival influences, and secure its regional interests, often in direct opposition to Sunni-majority states like Saudi Arabia. This network of alliances, built on the foundation of shared Shia identity, is a defining feature of Iran's complex and often controversial foreign policy.Global Shia Distribution: Iran in a Wider Context
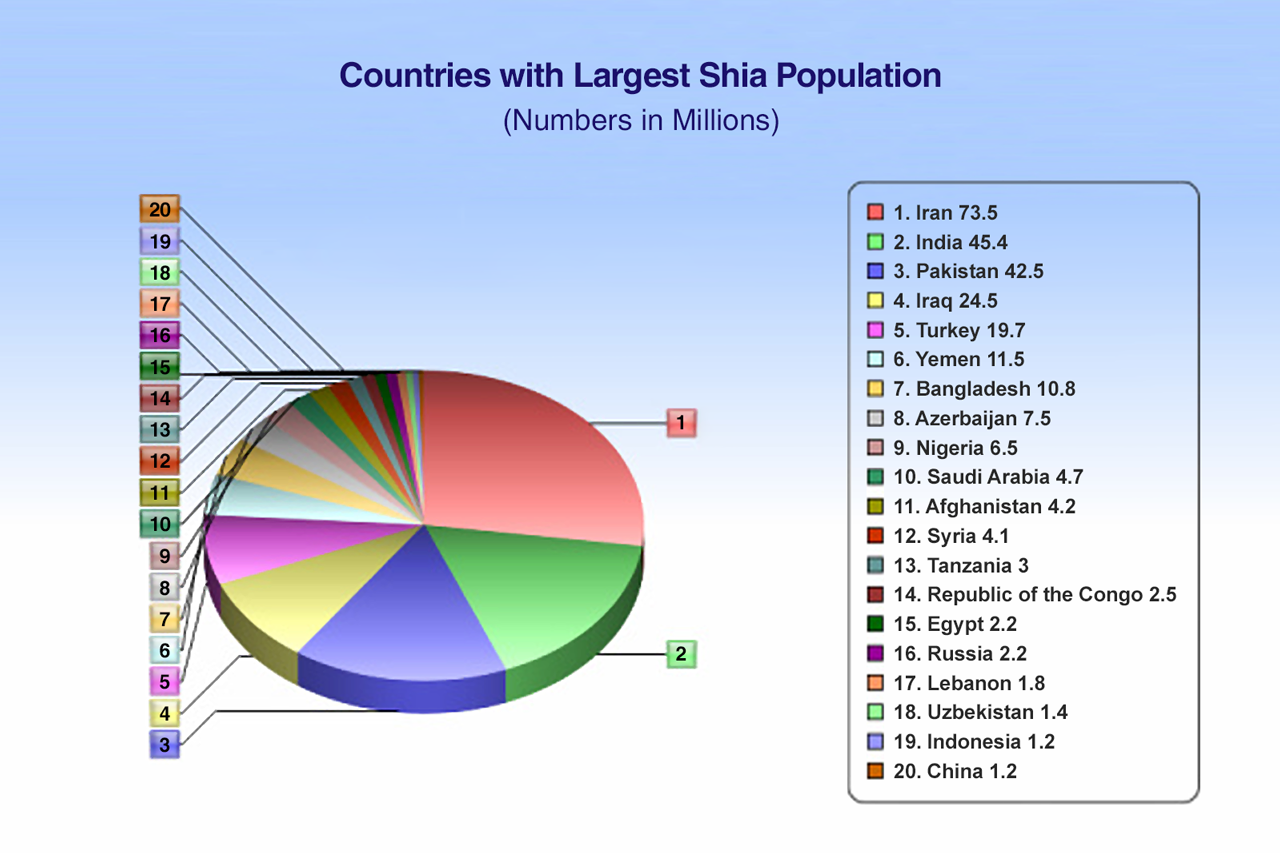
While Iran is the most prominent Shia-majority nation, understanding the global distribution of Shia Muslims provides crucial context for Iran's position in the world. Shia Muslims form a majority of the population in three countries across the Muslim world: Iran, Iraq, and Bahrain. Azerbaijan also has a Shia majority. Beyond these nations, the largest Shia populations are found in countries where they constitute significant minorities, such as Pakistan, India, Lebanon, and Yemen. In contrast, Sunni Muslims are the vast majority in most Muslim communities across Central Asia (including China), Europe (including Russia and the Balkans), South Asia, Southeast Asia, Africa, the Arab world, Turkey, and among Muslims in the United States. This global demographic landscape highlights Iran's unique position as a major Shia power in a predominantly Sunni Muslim world. The distinct historical, cultural, and theological identity of Shia Islam, separate from Sunni Islam, means that countries with significant Shia populations often share common perspectives and interests, creating a network that Iran frequently seeks to lead or influence.Understanding Iran's Religious Fabric: A Holistic View
The intricate tapestry of Iran's religious demographics, dominated by its vast Shia population, is far more than a simple statistical fact. It is a fundamental determinant of the nation's character, influencing its domestic governance, cultural expressions, and complex foreign policy. The overwhelming adherence to Twelver Shia Islam, institutionalized as the official state religion, shapes everything from legal frameworks to public holidays, embedding religious principles deeply into daily life. While the Shia majority is undeniable, the presence of Sunni minorities, often tied to specific ethnic groups like the Kurds and Turkmen, adds a layer of internal diversity and regional nuance. Furthermore, the strategic cultivation of ties with Shia communities and movements in other nations underscores how Iran's religious identity is a cornerstone of its regional and international engagement. To truly comprehend Iran, one must appreciate the profound and multifaceted impact of its Shia population, which serves as a constant and defining force in its historical trajectory and contemporary global role.We hope this comprehensive article has shed light on the significant role of the Shia population in Iran. Do you have further questions or insights on this topic? Share your thoughts in the comments below! If you found this article informative, please consider sharing it with others who might be interested in understanding the complexities of Iran and its unique religious identity. Explore more of our articles to deepen your knowledge of global demographics and geopolitical dynamics.
- Omg The Latest Nvg 2025
- Golden Tour Jungkook
- How To Make A Woman Queef
- Alana Cho Porn Leaks
- Best Shoes For Flat Feet Men
World Shia Muslims Population – Islamic Research and Information Center

Download wallpaper islam, shia, iran, section painting in resolution

Download wallpaper islam, shia, iran, section painting in resolution